The Bank of Japan head office in Tokyo.
Bloomberg|Getty Images
The Bank of Japan revealed Friday “higher versatility” in its financial policy– unexpected international monetary markets.
The reserve bank loosened its yield curve control– or YCC– in an unanticipated relocation with comprehensive implications. It sent out the yen whipsawing versus the dollar, while Japanese stocks and federal government bond costs moved.
In Other Places, the Stoxx 600 in Europe opened lower and federal government bond yields in the area leapt. On Thursday, ahead of the Bank of Japan declaration, reports that the reserve bank was going to discuss its yield curve control policy likewise added to a lower close on the S&P 500 and the Nasdaq, according to some strategists.
” We didn’t anticipate this type of fine-tune this time,” Shigeto Nagai, head of Japan economics at Oxford Economics, informed CNBC’s “ Capital Connection“
Why it matters
The Bank of Japan has actually been dovish for several years, however its transfer to present versatility into its until-now stringent yield curve control has actually left financial experts questioning whether a more considerable modification is on the horizon.
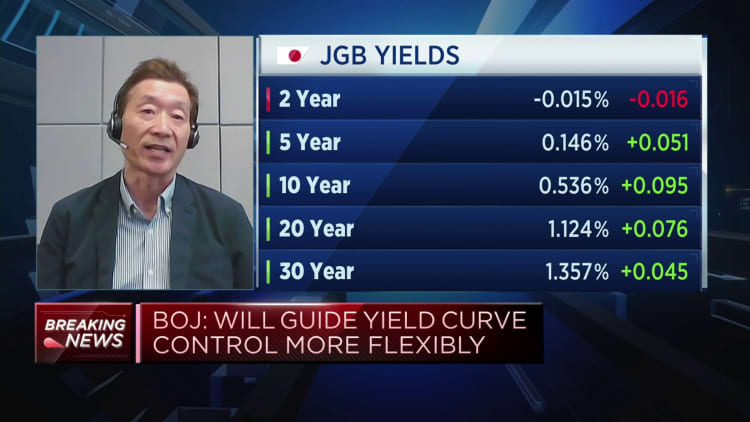
The yield curve control is a long-lasting policy that sees the reserve bank target a rate of interest, and after that purchase and offer bonds as required to attain that target. It presently targets a 0% yield on the 10-year federal government bond with the objective of promoting the Japanese economy, which has actually had a hard time for several years with disinflation.
In its policy declaration, the BOJ stated it will continue to enable 10-year Japanese federal government bond yields to change within the series of 0.5 portion point either side of its 0% target– however it will use to buy 10-year JGBs at 1% through fixed-rate operations. This efficiently broadens its tolerance by an additional 50 basis points.
” While keeping the tolerance band for the 10-year JGB yield target at +/ -0.50 ppt, the BoJ will enable more change in yields beyond the band,” financial experts from Capital Economics stated.
” Their objective is to boost the sustainability of the existing relieving structure in a positive way. Highlighting ‘incredibly high unpredictabilities’ in the inflation outlook, the BoJ argues that strictly topping yields will obstruct bond market operating and boost market volatility when upside threats emerge.”
Next action tightening up?
From a market viewpoint, financiers — a number of whom were not anticipating this relocation– were left questioning whether this is a simple technical modification, or the start of a more substantial tightening up cycle. Reserve banks tighten up financial policy when inflation is high, as shown by the U.S. Federal Reserve’s and European Reserve bank’s rate walkings over the previous year.
” Combating inflation was not the main factor for the policy fine-tune, as that would definitely suggest more powerful tightening up relocations, however the Bank acknowledged obstinately raised inflationary pressure by modifying up its projection,” Duncan Wrigley, primary China+ economic expert at Pantheon Macroeconomics, stated in a note.
The BOJ stated core customer inflation, omitting fresh food, will reach 2.5% in the to March, up from a previous quote of 1.8%. It included that there are upside threats to the projection, implying inflation might increase more than anticipated.
Kazuo Ueda, guv of the Bank of Japan (BOJ).
Bloomberg|Bloomberg|Getty Images
Speaking at a press conference after the statement, BOJ Guv Kazuo Ueda soft-pedaled the transfer to loosen its yield curve control. When asked if the reserve bank had actually moved from dovish to neutral, he stated: “That’s not the case. By making YCC more versatile, we boosted the sustainability of our policy. So, this was an action to increase the possibility of sustainably attaining our rate target,” according to a Reuters translation.
MUFG stated that Friday’s “versatility” fine-tune programs the reserve bank is not yet all set to end this policy procedure.
” Guv Ueda explained today’s relocation as boosting the sustainability of financial relieving instead of tightening up. It sends out a signal that the BoJ is not yet all set to tighten up financial policy through raising rate of interest,” the bank’s experts stated in a note.
Capital Economics’ financial experts highlighted the value of inflation figures looking ahead. “The longer inflation stays above target, the bigger the possibilities that the Bank of Japan will need to follow up today’s tweak to Yield Curve Control with a real tightening up of financial policy,” they composed.
However the timing here is vital, according to Michael Metcalfe of State Street Global Markets.
” If inflation has actually undoubtedly gone back to Japan, which our company believe it has, the BoJ will discover itself requiring to raise rates simply as wish for rate of interest cuts increase somewhere else. This must be a medium-term favorable for the JPY [Japanese yen], which stays deeply underestimated,” Metcalfe stated in a note.
Completion of YCC?
The efficiency of the BOJ’s yield curve control has actually been questioned, with some specialists arguing that it misshapes the natural performance of the marketplaces.
” Yield curve control is an unsafe policy which requires to be retired as quickly as possible,” Package Juckes, strategist at Societe Generale, stated Friday in a note to customers.
” And by anchoring JGB (Japanese federal government bond) yields at a time when other significant reserve banks have actually been raising rates, it has actually been a significant consider the yen reaching its most affordable level, in genuine terms, given that the 1970s. So, the BoJ wishes to extremely thoroughly take apart YCC, and the yen will rally as gradually as they do so.”
Pantheon Macroeconomics’ Wrigley concurred that the reserve bank is aiming to move far from YCC, explaining Friday’s relocation as “opportunistic.”
” Markets have actually been fairly calm and the Bank took the chance to capture most financiers by surprise, offered the agreement for no policy modification at today’s conference,” he composed.
” The marketplaces are most likely to check the BoJ’s willpower, as it most likely will look for to craft a steady shift far from its [yield curve control] policy over the next year approximately, while leaving the short-term rate target the same, as it still thinks that Japan requires helpful financial policy.”
— CNBC’s Clement Tan added to this report.