A item technique is a roadmap for establishing and providing an item to market. It allows positioning in between item management, task management, and item style, and makes sure that the item supports service goals. Designers might not be accountable for establishing the item technique, however their work and successes are undoubtedly affected by it, particularly if they operate in growth-driven and lean environments
As an item designer who has actually constructed a number of web and mobile options on cross-functional item groups, I understand the indications of a stopping working item technique. In this post, I share those warnings and talk about with other Toptal specialists how designers can assist their groups conquer those drawbacks.
Warning No. 1: Doing Not Have a Clear Item Vision
The most crucial factor to consider when crafting an item technique is the item vision A robust and distinct item vision assists groups set a supreme objective, offers a sense of function, develops positioning, and prevents technique issues from the start. When problems do emerge, the item vision functions as a north star, assisting groups back to base.
The item vision is the long-lasting goal for the item and can be specified through an item vision declaration that interacts the item’s objectives to stakeholders. For instance, eBay’s vision declaration for commerce includes “allowed by individuals, powered by innovation, and open up to everybody.” On the other hand, bad vision declarations create confusion for groups and stakeholders, and do not have clear focus and instructions for business.
Without a clear item vision, it is difficult for anybody (company owner, designers, designers) to see the huge photo. Groups might wind up altering course while disagreeing on how finest to move on. So how do you make sure that everybody is heading towards the exact same location?
Item Method Option: Procedure Your Item’s Success
An item vision ought to be specified from the start Nevertheless, to keep an item group on the best track, the item vision need to be reviewed and examined throughout the item life process These little modifications typically result in considerable enhancements
As the item grows and markets modification, groups need to constantly determine an item’s success to prevent a stagnant item vision. This is where item success metrics get in the photo.
Item success metrics supply unbiased insights that assist a business anticipated an item’s making possible and determine its engagement efficiency. For example, client life time worth is a formula that forecasts just how much profits somebody will create throughout their time as a paying client, while bounce rate procedures the number of individuals leave a website or app after checking out a single page. Normally speaking, they are determined by the item supervisor. Nevertheless, as an item designer, you might be asked to assist determine UX success metrics to comprehend how users browse digital items and deal with style defects.
There are 2 kinds of UX success metrics: behavioral (what users do), such as time on job, and attitudinal (what users state), such as the client fulfillment rating.
Item and UX success metrics have the possible to provide important insights and make sure that item objectives stay lined up with the item vision. Nevertheless, for metrics to be significant, they need to be actionable, available, and auditable When identifying which metrics to determine, think about asking these concerns:
- What kind of metric finest matches my item?
- Where is my item in the life process?
- Who are the stakeholders for these metrics?
Warning No. 2: Permitting Consumer Demands to Bypass Item Requirements
The trick to crafting an item technique that provides useful options begins with a clear understanding of the item requirements, the encapsulation of an item’s functions, functions, and habits. It does not depend on providing unnecessary concern to client demands– inquiries about sales or functions that are not always based upon the thorough objective of the item.
While client demands are incentives that drive a client to purchase or utilize a product and services– such as the desire for a smart device upgrade for access to more feature-rich applications– item requirements are requirements that are clearly articulated through marketing research, such as the requirement for extra smart device storage and higher performance. Consumers are requiring by nature, and although we ought to be understanding to their requirements, a strong item technique can not always accommodate every client demand.
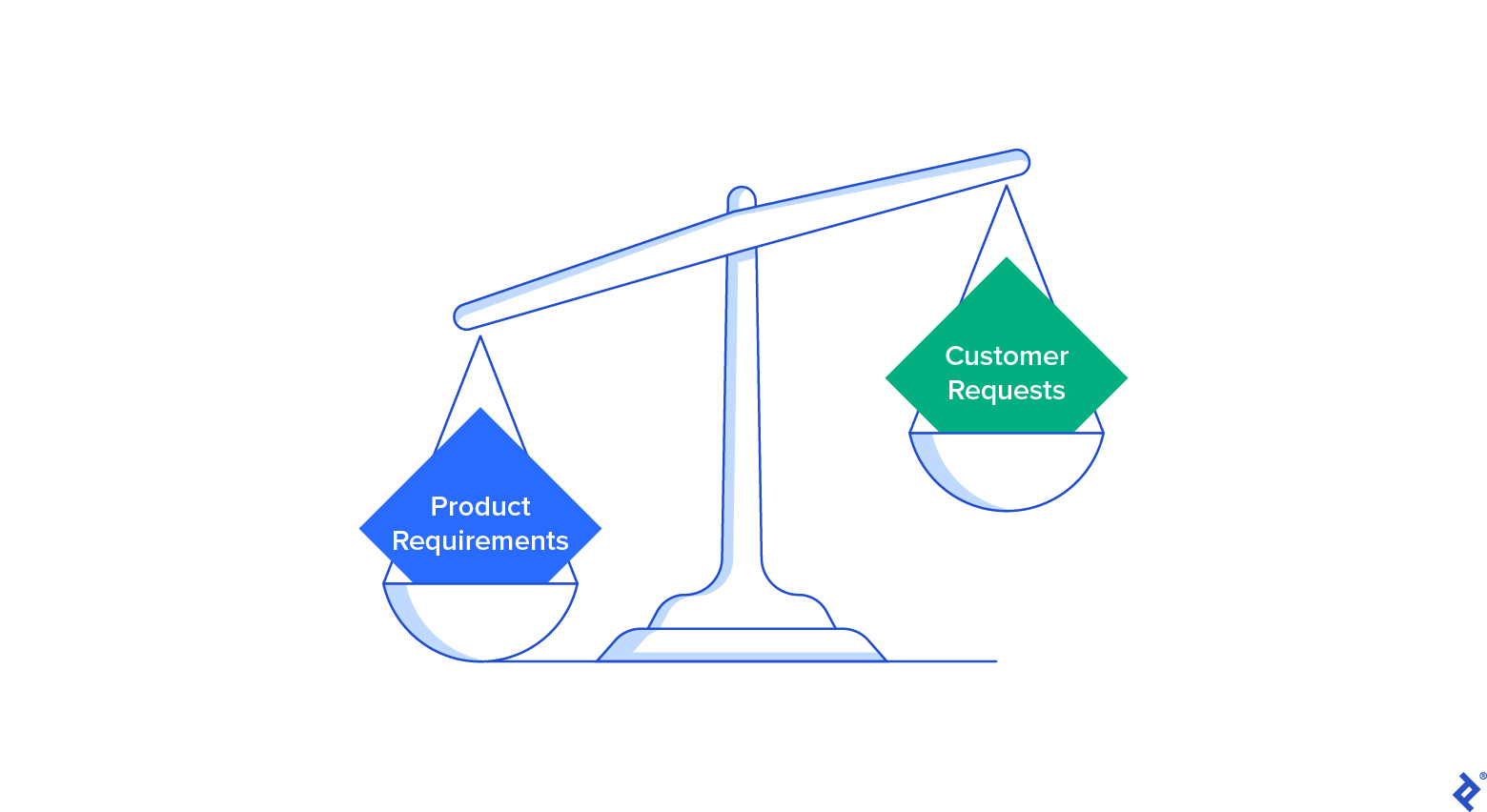
Toptal item and task management professional Milos Belcevic states that the difficulty presented by attempting to balance requirements and demands can be an expression of an imbalance in between the pursuit of item quality and client intimacy Item quality is a structure that focuses on rapidly establishing and providing items that surpass client expectations. Consumer intimacy is the practice of engaging with private clients to accommodate their requirements and increase their item commitment.
Neither of these methods is always remarkable to the other, however discovering a rational balance in between the 2 is crucial to handling client demands in time.
Item Method Option: Carry Out UX Analysis to Evaluate Consumer Demands
In some cases client demands wind up exceeding item requirements due to the fact that of an absence of appropriate UX analysis Without it, the item group might establish functions and performances to satisfy one-off client or management demands that are not really considerable to the total item technique. Simply as it’s an engineer’s duty to press back versus an inferior style, it’s a designer’s duty to withstand inadequately developed and difficult demands.
Belcevic recommends utilizing chance mapping to examine and focus on brand-new demands based upon service objectives and client research study. It’s likewise reasonable to think about the factor behind a client demand. It’s a lot easier for a client to determine an issue than for the item group to discover an option. Recognizing the underlying issue might result in a far remarkable treatment than what was asked for. Examining potential users with UX methods like personalities and compassion mapping can likewise assist item designers much better determine their core item users and comprehend their requirements and habits.
When I worked as an item designer for Chaka, an online financial investment platform, we cultivated our user neighborhood to make sure that our item technique was lined up with our clients’ requirements. We dealt with a brand-new item based at first on examining spaces in our existing item set. To show out our concepts, we initially examined our clients’ desire to acquire, their capability to accept danger, and the sort of portfolios they ‘d wish to develop.
To collect this info, we developed weekly sessions with the client group. This permitted us to communicate with our clients throughout the item meaning and prototyping stages. Of the 7,000 users we dealt with prior to advancement, more than 5,000 registered for the item as an outcome of our ongoing interactions with them. By the time we released, 10,000 existing clients had actually registered through the business’s Telegram channel. I consider this a strong sign of a effective item technique that stabilizes service objectives and client demands.
Warning No. 3: Misinterpreting Functions for Worth
Another indication of a stopping working item technique is misinterpreting great deals of functions for item worth. For digital items, functions may be an application’s performances, abilities, or visual qualities, such as item filtering, desire lists, and checkout on an e-commerce site
Structure a digital service with unneeded or low-value functions can lead to providing items to market that are too made complex to utilize, a phenomenon called function creep Extreme varieties of functions, or the incorrect functions, are related to greater style and application expenses, lower returns from those functions, and increased client discontentment in the function set.
According to Toptal multidisciplinary designer Austine Eluro, a lot of functions are an uncomfortable indication of scattered item technique. He states, “If you include a lot of functions to a single application, you develop a center that can do whatever however can not please anyone. No item can be all things to all individuals.”
Some companies end up being called “ function factories,” business that reward function amount and do not stop to examine potential functions’ worth so long as they suit the advancement schedules. For digital items, “ bloatware” is a comparable phenomenon: undesirable and possibly damaging apps come pre-installed on gadgets. The majority of these apps are never ever utilized, users didn’t request for them, and they typically can’t be uninstalled. A brand-new wave of bloatware elimination tools has actually been produced to tackle this issue.
Melissa Perri explains this failure mode in her book Leaving the Build Trap, advised by Belcevic. In her book, Perri states that when business stop working to comprehend their clients, they can’t supply genuine worth. They change real understanding with a streamlined metric based upon functions delivered, which develops an incorrect meaning of worth. Organizations fall under the “ develop trap” when they begin officially determining success in regards to output volume rather of by result.
Item Method Option: Carry Out a Reliable Prioritization Structure
Prioritization assists make sure that item groups are dealing with the most pertinent functions and preventing inefficient practices. Think about asking these concerns about all potential functions:
- Is this function important to the end user?
- Is it vital to the product/business goal?
- Do the advantages surpass the expense and intricacy of style and application?
If the response to these concerns is no, you ought to omit the function from your item technique or delay it for future factor to consider.
I suggest likewise utilizing an official prioritization structure to assess brand-new functions reasonably and regularly in the item technique roadmap Item prioritization has actually notoriously been a subject of confusion for item groups, and often a more clinical technique is needed.
As an item designer, I have experience utilizing the MoSCoW, RICE, and Kano prioritization structures. For example, at Chaka we utilized MoSCoW to assist narrow our function set when dealing with considerable time restraints. I produced MoSCoW quadrants and outlined our clients’ requirements (based upon research study) in should have (M), ought to have (S), might have (C), or will not have (W). This assisted us decrease our functions in simply a couple of hours.
Warning No. 4: Experiencing Interaction Breakdowns
In item technique advancement, there are lots of stakeholder inputs and viewpoints to handle, and interaction issues might emerge. A few of these issues happen due to the fact that task function meanings can differ drastically from business to business and even from task to task. For instance, some item supervisors are technical and concentrate on engineering; some are designers and appoint themselves prototyping obligations; and some focus more on marketing, item life process, or users. When you sign up with a task as a designer, it is essential to figure out the limitations of your function to prevent disputes with other staff member and make sure that every stage of the task is executed properly.
This sort of function clearness problem can normally be attended to in advance by clarifying the chain of reporting and making sure that all task functions are plainly specified through methods such as group discovery Nevertheless, other interaction problems and disputes can emerge throughout a task, such as misconceptions, absence of feedback, and operating in silos. Among the most typical dispute locations is in between the item supervisor and the UX designer Both are worried about user experience and the relation of requirements to user requirements, however they might approach issues in a different way.
Item Method Option: Enhance Item Vision and Foster Conflict-resolution Methods
Group positioning is essential for reliable interaction within a cross-functional item group to make sure that the item technique takes precedence. For beginners, I suggest working together throughout groups to develop the item vision instead of permitting a single person or little group to enforce their concepts on the entire group. An excellent way to make sure openness within cross-functional groups is to show your item vision declaration on the workplace wall (for internal groups) and as part of business wikis and internal understanding bases, such as Confluence.
Naturally, disputes will likely happen throughout any task. Disputes aren’t the issue; issues emerge when disputes aren’t effectively fixed. Within many Nimble structures, there are basic patterns for dispute resolution and function meaning. This may begin with making sure that staff member with various functions (e.g., item supervisors, item owners, Scrum masters, item designers) work together in the early ideation and item meaning phases. Towards completion of a task, groups can deal with disputes by participating in and taking part in a retrospective conference to discuss what worked out and what can be enhanced.
Warning No. 5: Allowing Unnecessary Resource Loading
Resource filling is an important aspect of resource preparation for any item group. Because it affects every employee, it is very important to acknowledge when there’s an issue with it. Resource overwhelming– when there are a lot of jobs for the readily available resources– is a clear indication of a stopping working item technique. In some cases a task feels strained with issues from the start, even prior to client demands and advancement models have actually had an opportunity to affect requirements. Other resources apart from style, like engineering, screening, and marketing, might separately or jointly be extended to a snapping point with ensuing damage done to the style procedure.
Eluro states that issues with load can emerge when item groups stop working to acknowledge a task’s success. “Some groups neglect success signs. When the item has actually been released, they neglect the success that that item has really accomplished. It’s insufficient to concentrate on faults.” He states acknowledging success can supply instructions for future requirements, whereas focusing just on faults or spaces in protection can result in a scattered advancement focus and extreme work.
Item Method Option: Develop an MVP Model
I constantly like to begin the style procedure with a minimum feasible item (MVP) model to decrease expenses and time to market. Item designers typically develop models to determine issues, establish options, and share styles with stakeholders without unneeded resource expense.
The kind of model you choose to develop will depend upon where you discover yourself within the item advancement life process. In early advancement, you might develop a low-fidelity, fixed model or wireframe utilizing low-cost, easily offered products. Lo-fi wireframes consist of easy graphes of on-screen UI components and material hierarchy. Later on, designers develop high-fidelity, interactive mock-ups to picture the characteristics and interactive functions of the item in more information. These models are generally utilized to check the item’s abilities prior to advancement.
Quick MVP prototyping is a specific technique utilized in lean environments that allows reliable early feedback from stakeholders and end users. MVP models assist groups attain an early win and can be turned into released items incrementally even in case of decreases in resources and schedule cuts.
A Robust Item Vision Assists You Construct a Fail-proof Item Method
There are lots of methods for an item technique to stop working, however all effective item methods have something in typical: a clear item vision. The item vision ought to be established as a collective effort in between the item group and the item designer, including client and end-user input as early as possible.
When developing an item, issues are undoubtedly going to happen. Nevertheless, with a distinct item vision, a clear understanding of the item requirements and functions, and understanding of conflict-resolution methods, it will be much easier to establish and execute enduring options.